IS CBD LEGAL? – Everything You Need to Know
CBD products have drastically increased in availability and popularity over the last year. The only thing growing faster than CBD appears to be confusion and curiosity over what exactly it is and who it’s meant for. Whether you’re already a consumer or just CBD curious, this little chunk of words will help you cut through the misinformation and help you catch up to speed.
CBD is short for cannabidiol, is one of the 113 cannabinoids molecule found in the cannabis plant in 1940.
NOTE: It should not be mistaken for Cannabinol or Cannabinodiol.
In 2018, clinical research on cannabidiol showed its usage in suppressing anxiety, improving cognitive abilities, helps in correcting movement disorders, and reducing pain.
Cannabidiol can be absorbed into the body through different mediums:
- Inhalation of cannabis smoke or vapor;
- as an aerosol spray into the cheek;
- and by mouth.
CBD may be supplied as CBD oil containing only cannabidiol as the active ingredient that means no included Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol [THC] or terpenes), a full-plant CBD-dominant hemp extract oil, capsules, dried cannabis, or as a prescribed liquid solution.
THC is also one of the cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant, and probably the most popular because of its psychoactive properties as it is the main element in Marijuana, it’s the one that gets you “high.” CBD is becoming more relevant and gaining more ground because of its potential therapeutic benefits. CBD does not have the same psychological effect as THC, and it may change the impact of THC in the body if both are present. As of 2018 research, the mechanism of action for its biological effects has not been determined.
Every variety of the cannabis family produces certain cannabinoids (hemp included). While CBD and THC are the most famous cannabinoids, there are many different types (113), and only recently have significant resources been put into their study and research. Our brains have specific receptors designed for accepting cannabinoids, CB1, and CB2. These receptors are majorly responsible for the assimilation of cannabinoid molecules into your system, resulting in the psychoactive (“high”) and immune responses correlated with cannabis consumption.
Research Studies on CBD
Dr. J H Atkinson, co-director of the Center for Medical Cannabis Research(CMCR), University of California, San Diego, says, “There is a great deal of interest in the possible therapeutic impacts of CBD, but there is a very little evidence of an adequate result to be produced.” CBD may have certain health benefits, but the lack of research in this aspect means there aren’t enough data to support most of the unreliable claims. Along that same line, the lack of analysis also indicates the health risks of consuming CBD are unclear.
Some research suggests that CBD may suppress anxiety and self-depressing thoughts, and there’s evidence that CBD has antipsychotic effects in people with schizophrenia. But other studies have shown no significant benefit of CBD over a placebo.
Scientific observation and hypothesis take time, and the research community has only just begun to pursue an experimental inquiry into the distinct effects of various cannabinoids. That said, many researchers believe that the potentials of CBD are promising.
Is CBD legal?
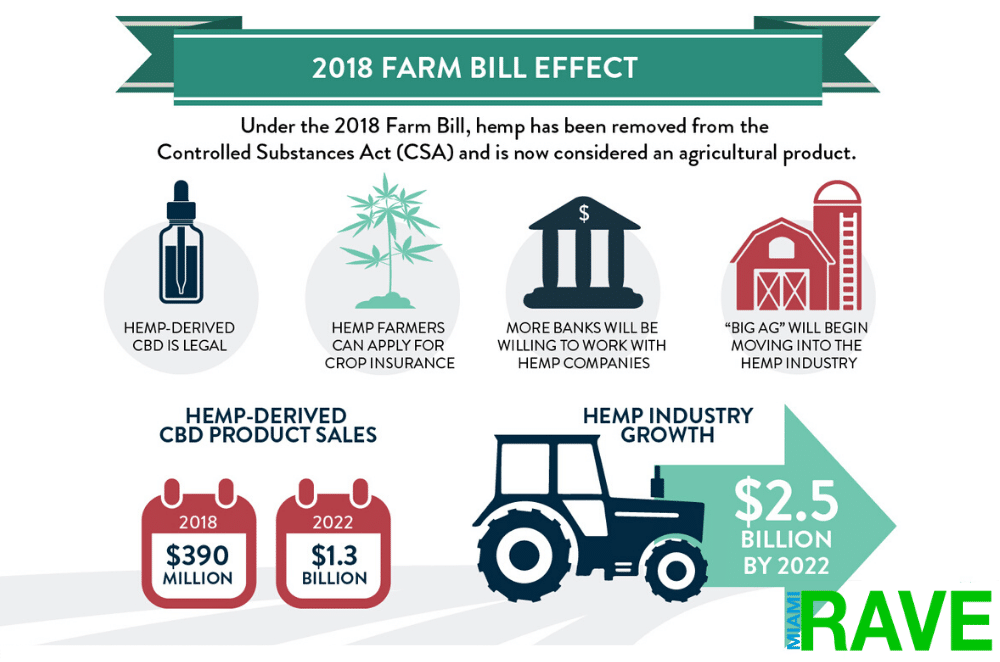
CBD, after its explosion into the market, left a lot of consumers and researchers confused. Everybody asking the same questions, “Is CBD legal?” Technically, the answer is YES, but it isn’t quite so cut and dried. All thanks to the passage of the 2018 US farm bill that legalized the industrial use of hemp and the legalization of medical and recreational cannabis at the state level.
The cannabis plants are in many different varieties. For past decades though, the US Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) treated them all the same, classifying cannabis as a Schedule substance. Schedule drugs are considered to currently have no accepted medical use and a high potential for abused usage, thus, illegal to produce or even possess.
However, thanks to the Agriculture Improvement Act of 2018 (aka the Farm Bill), it changed all that. The Farm Bill nationally legalized “hemp,” which, as defined by the legislation, is cannabis that contains nothing more than 0.3% of THC. Cannabis that contains a higher level of THC is thereby listed as “marijuana” and remains illegal.
In other words, if a CBD product is produced from any hemp plant, it’s therefore legal, if it comes from a marijuana plant, then, it is federally illegal, despite the local laws. And even when it comes from a hemp plant, there’s still no hundred percent certainty it won’t contain THC, thanks to things like cross-pollination and the absence of industry regulation.
The Food and Drug Administration(FDA) is currently trying to figure out how to regulate CBD, which now falls under their investigation. Temporarily, experts recommend buying CBD products from manufacturers located in Indiana and Utah. They are states that require cannabis products to be tested for potency and purity before marketing.
If you’re confused about if the CBD products flooding your city or town are legal or shady, this is where you should be. CBD is right at the center of a complicated legal tangle in constant flux. Here’s what we currently know and what’s accurate at publication date.
What The Federal Law Says about CBD:
The federal government identifies two forms of the ‘Cannabis sativa’ plant; hemp and Marijuana. Hemp contains high levels of cannabidiol (CBD), the compound in cannabis known for its medicinal properties, and traces of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the psychoactive component in Marijuana that causes the “high.”
It is the least processed or produced form of the cannabis plant.
On the other hand, Marijuana is increasingly being bred to contain higher levels of THC, sometimes upward of 30 %, and lower levels of CBD an average of less than 0.2 percent, according to research made.
In 2018, the Agriculture Improvement Act, known as the Farm Bill, legalized CBD derived from a hemp plant and contains no more than 0.3% THC (by dry weight). CBD that comes from the marijuana plant continues to remain illegal under the Controlled Substances Act since the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) classifies Marijuana as a Schedule-1 drug in the DEA dialect, which means the administration believes its medical use is not currently accepted, hence, high potential for abuse.
The Farm Bill also made regulations for hemp farmers, which means, that any cannabinoids that are derived from a hemp plant will be legal, if and only if that hemp is produced in a manner such that it is consistent with the Farm Bill and adheres to the rulings of association state regulations, associated federal laws, and must be by a licensed grower. According to the Brookings Institute, it must also be a non-profit public policy organization.
This shows that even if a CBD product contains the right amount of THC but was grown by an unlicensed producer, it’s still illegal.
CBD is yet to be approved as a dietary supplement or food ingredient by the FDA. This is because CBD is also an approved prescription drug (Epidiolex), the FDA still considers CBD as only a drug ingredient, which means it cannot be marketed and sold as a dietary supplement or food-related parts with therapeutic properties (or even shipped across state lines) without first going through the FDA’s drug approval process regardless of whether the products are derived from hemp or not.
So, what about all the CBD oils, pills, edibles, and currently in the market that claim to fight anxiety, suppress pain, and curb the spread of cancer? That’s what the FDA is trying to figure out now.
None of these products have been declared as safe or effective. The power to give CBD the approval is bestowed upon the FDA, and they are currently considering to do that.
In the meantime, it’s unclear as to whether the agency will crackdown on violators of the regulation. According to the FDA, the agency considers a lot of factors when deciding whether or not to start-up an enforcement action, including agency resources and the threat to public health-wise.
What State Laws Say About CBD
Although hemp-derived CBD is federally legal now, many states and cities are updating their bills, but they’re not always in concurrence with regulations at the federal.
For instance, Products with any amount of THC is still illegal in Texas; Colorado has recently made it legal to use all the parts of the hemp plant as a food ingredient.
Note Majorly that CBD is not legal in all 50 states.
The best way to figure whether CBD products are legal in your state is to become familiar with local laws of cannabis.
Organizations like the Marijuana Policy Project, the National Conference of State Legislatures(NCSL), and the National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws maintain databases and interactive data visualizations. For the most up-to-date information, check the state’s criminal code or agriculture department.
Finding approved CBD products
With local and federal cannabis regulations still contrasting, finding CBD products that have the lowest legal risk requires a bit of a tiring experience. Experts recommend being diligent about checking the content of product labels and manufacturers’ websites or sales page for any product to understand what the product actually contains.
Here’s what to look for:
- The nation of Origin of hemp: Look for products made from hemp grown in the US. Hemp that is grown overseas is at the mercy of that country’s production rules and regulations or lack thereof.
- Certificate of analysis: This document is also called a COA; it shows the results of independent laboratory testing that checks for things like potency and contaminants. Check for the batch number on the COA, and it should match the number on the product’s label or packaging. Some states make it easier to find this information. For instance, in Indiana, it is required that all CBD products include a QR code on their label that allows users to scan and download the COA to their phones.
- Testing methods: When scanning for the COA, you have to make sure that the laboratory doing the testing meets the “ISO 17025” standards. The testing methods should also have been verified by one of three national regulatory organizations: the Association of Official Agricultural Chemists, the US Pharmacopeia, or the American Herbal Pharmacopoeia.
- Potency: The COA should also affirm that the product so contains the amount of CBD and THC as listed on its label by dose and in total.
If a manufacturer doesn’t have this information or isn’t willing to share it, you should avoid purchasing their products. Not only could you be indirectly breaking the law by buying it, but research also shows that it’s common for CBD products to be mislabeled, meaning they could be getting more THC than you hoped or too little CBD to make the product useful. You can always check out the approved CBD products available here on Miami Rave.
How Is CBD Used?
CBD is available in various forms. The delivery method of CBD affects the speed of the effect and how it acts on the body. The use of CBD is majorly dependent on the personal needs and preferences of the user.
CBD is available in different forms, including oils and tinctures.
Delivery Methods of CBD:
- Edibles: CBD can be put into products to dine and wine, like gummies, fruits, chocolates. Edibles can take anywhere between 20 minutes to 4 hours to take effect.
- Oils and tinctures: They are gotten when CBD is processed and concentrated, often placed under the tongue using a dropper and absorbed into the bloodstream.
- Pills and capsules: CBD can be made into solid pellets and tablets ingested orally and look similar to the vitamins and drugs you’d find in a drugstore. They usually contain CBD oil or CBD isolate.
- Topicals: These are oils, creams, and lotions, infused with CBD, that are intended to be used directly on skin, hair, or nails. CBD is a popular way to treat localized pain but are also used as skincare, hair care, and massaging oils as well.
- Vaping: This is delivered like cigarettes; it involves inhaling a vaporized liquid containing CBD oil. Nicotine is not usually in this mixture if CBD is, though it is still possible to mix them.
What Are The Health Benefits Of CBD?
CBD is marketing as a bit of a remedy to all, with manufacturers claiming it can do everything from relieving anxiety to curbing the spread of cancer. Moreover, cannabis’s classification as a Schedule-1 drug has severely hampered American scientists’ ability to study CBD, making it hard to support or refute these claims. The available studies tend to be small or are done on animals or in laboratories.
That said, CBD seems promising. Early experiments suggested that it may help fight against anxiety, ease the symptoms of schizophrenia, and reduce pains (though the latter is often done in conjunction with THC).
The most reliable evidence of CBD’s effectiveness, though, is concerning epilepsy. Just last year, the FDA approved Epidiolex, a medication used to treat Lennox-Gastaut and Dravet syndromes, two rare and severe forms of epilepsy. It was the first approval of a cannabis-derived drug by the agency.
At What Risk Do You Take CBD?
World Health Organization found, in a 2017 report, that CBD, in its pure state, is safe, well-tolerated by humans and animals, and not likely to cause physical dependence or abuse or influence psych activity. And according to NIH, the National Institutes of Health, 1,500 milligrams of CBD have been taken safely by mouth every day for a total of four weeks.
CBD oil for anxious pets is likely safe, although research is yet to prove that it helps.
With that been said, there are still a few risks associated with taking CBD that you should know, as thus :
- The Side Effects: Low blood pressure, dry mouth, drowsiness, and lightheadedness have been reported, according to the NIH, as signs similar to that of liver injury, though drowsiness is less rampant.
- Limited Research: CBD’s classification as a Schedule-1 drug severely limits the amount of studies researchers can conduct on the compound to a shallow minimum. What does exist and its results so far are promising, but there are still a lot of unknowns around things like; what conditions it actually could help treat and the quantity that people would need to take for it to be effective. That means if you’re taking CBD to address a particular ailment, at this time, you could be either taking too much, too little or wasting your money altogether.
- Inadequate Regulation: There are no standards set in place for the production, testing, or labeling of CBD products, which makes any federal oversight or quality control quite impossible. Researchers from Penn Medicine found that nearly 70 percent of CBD products purchased from the untrusted internet contained either more CBD than the label indicated, which could be dangerous or less CBD than was reported, which could reduce any potential actions. Many of these products also contained significant levels of THC.
- Drug interactions: Little is known about how CBD could interfere with other medications. Still, experts say it may interfere with the speed at which the body breaks down a variety of prescription medications, which can increase the side effects mentioned above. It can also influence the sedative properties of herbs and supplements known to cause drowsiness or sleepiness. Talk to a doctor to confirm if anything you take regularly could be affected by CBD.
- Pre- and post-natal unknowns: There’s no sufficient evidence yet about whether it’s safe to take CBD while during pregnancy or nursing. Experts strictly advise women to avoid it at those times.
The information here is for commercial and informational purposes only and is not intended for use as health or medical advice. We strongly recommend that you should always consult a physician or other qualified health official regarding any questions you may have about any medical condition or health objectives. Please always contact us for more information and inquiry when you need to.